Policy-Based Routing OpenWrt Package Documentation
- Relevant
pbrversion - Version 1.1.8
- Version 1.1.6
- Gateways/Tunnels
- IPv4/IPv6/Port-Based Policies
- Domain-Based Policies
- Physical Device Policies
- DSCP Tag-Based Policies
- DNS Policies
- Fw4 Nft File Mode
- Custom User Files
- Strict Enforcement
- Use Resolver’s Set Support
- Customization
- Other Features
- How It Works (
nftmode) - Processing Policies
- Processing DNS Policies
- Policies Priorities
- Processing Custom User Files
- How To Install - OpenWrt 23.05 and newer
- How To Install - OpenWrt 22.03 and older
- Requirements
- How to install dnsmasq-full
- Unmet dependencies
- How to upgrade to a most recent version
- Helpful Instructional Videos
- Service Configuration Settings
- Example Policies
- Example OpenWrt Configurations for More Complex Cases
- A Word About Default Routing
- A Word About Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 App
- A Word About DNS-over-HTTPS
- A Word About HTTP/3 (QUIC)
- A Word About IPv6 Routing
- A Word About Routing Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu Traffic
- A Word About Interface Hotplug Script
- A Word About Broken Domain Policies
- First Troubleshooting Step
- Warning: Please set ‘dhcp.lan.force=1’
Notable version changes
Relevant pbr version
This README is relevant for the pbr version 1.1.8. If you’re looking for the README for the newer or older version of pbr, please check the README links within the luci-app-pbr.
Version 1.1.8
- This release completely drops the iptables/ipset (and resolvers using ipset) support.
- This release uses the fw4 nft file mode by default.
- The Wireguard Server & Client user script integrated into the
pbrservice, if Wireguard servers are discovered, their routing is automatically configured to go over WAN. - To enable targeting a Wireguard server tunnel, explicitly add its interface name to supported_interface option.
- If the directory
/etc/pbr.d/exists, all the files in that directory are processed as custom user files without the need to add them topbrconfig. - The
procd_lan_deviceconfig list allows you to override the default device (br-lan) used for LAN interface detection.
Version 1.1.6
- This release has separate code for nft- and iptables-capable versions, the nft version (
pbrpackage) no longer supports resolver options with ipset. - The WAN interface name is no longer auto-detected. If you use a non-standard name for WAN interface, you can set it in options.
- If you use a non-standard name for LAN interface you can set it in options.
- A new feature of DNS Policies (also see Processing DNS Policies) was added to help ensure name resolution is sent to a specific resolver when needed.
Description
This service allows you to define rules (policies) for routing traffic via WAN or your L2TP, OpenConnect, OpenVPN, PPTP, Softether or WireGuard tunnels. Policies can be set based on any combination of local/remote ports, local/remote IPv4 or IPv6 addresses/subnets or domains. This service supersedes and obsoletes the VPN Bypass (README at GitHub/README at jsDelivr) and VPN Policy Routing (README at GitHub/README at jsDelivr) services.
Features
Gateways/Tunnels
- Any policy can target either WAN or a VPN tunnel interface.
- L2TP tunnels supported (with protocol names l2tp*).
- OpenConnect tunnels supported (with protocol names openconnect*).
- OpenVPN tunnels supported (with device names tun*).#1 #2
- PPTP tunnels supported (with protocol names pptp*).
- Tailscale tunnels supported (with device name tailscale*).
- Tor tunnels supported in nft mode only (interface name must match tor).
- Wireguard tunnels supported (with protocol names wireguard*).
IPv4/IPv6/Port-Based Policies
- Policies based on local names, IPs or subnets. You can specify a single IP (as in
192.168.1.70) or a local subnet (as in192.168.1.81/29) or a local device name (as innexusplayer). IPv6 addresses are also supported. - Policies based on local ports numbers. Can be set as an individual port number (
32400), a range (5060-5061), a space-separated list (80 8080) or a combination of the above (80 8080 5060-5061). Limited to 15 space-separated entries per policy. - Policies based on remote IPs/subnets or domain names. Same format/syntax as local IPs/subnets.
- Policies based on remote ports numbers. Same format/syntax and restrictions as local ports.
- You can mix the IP addresses/subnets and device (or domain) names in one field separating them by a space (like this:
66.220.2.74 he.net tunnelbroker.net). - See Policy Options section for more information.
Domain-Based Policies
- Policies based on (remote) domain names can be processed in different ways. Please review the Policy Options section and Footnotes/Known Issues section, specifically #5 and any other information in that section relevant to domain-based routing/DNS.
Physical Device Policies
- Policies based on a local physical device (like a specially created wlan). Please review the Policy Options section and Footnotes/Known Issues section, specifically #6 and any other information in that section relevant to handling physical device.
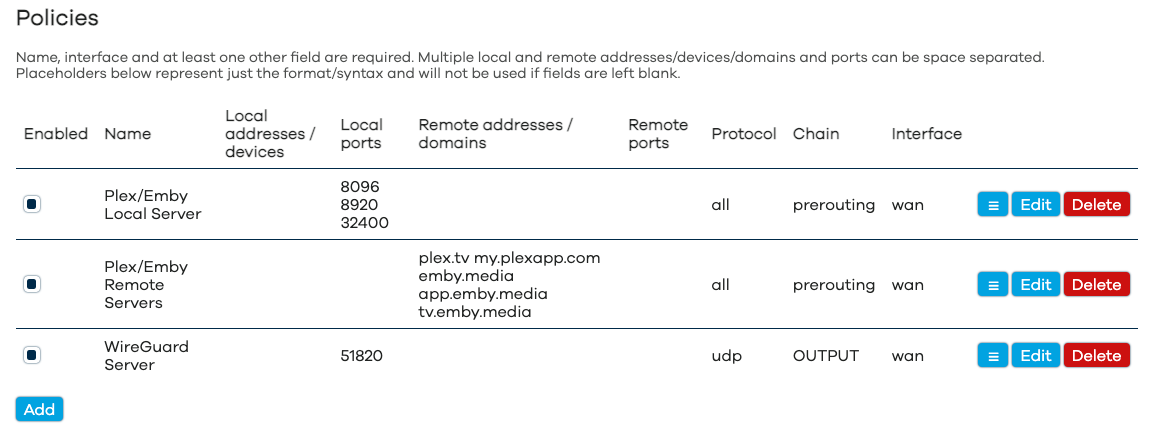
DSCP Tag-Based Policies
You can also set policies for traffic with a specific DSCP tag. On Windows 10, for example, you can mark traffic from specific apps with DSCP tags (instructions for tagging specific app traffic in Windows 10 can be found here).
DNS Policies
Use of DNS Policies allows to route the name resolution (DNS) requests from local devices/IP addresses or MAC addresses thru a specific DNS server. Either the first DNS server from a specified interface or a specific DNS server indicated by its IP address can be used. Please note that the use of DNS Policies will override local DNS Hijacking (if enabled) and also will prevent the domain-based policies from working for the local devices specified in the DNS Policy, as your dnsmasq will not be queried by those local devices anymore.
Fw4 Nft File Mode
This mode is the only operating mode in version 1.1.7. Instead of translating each policy into one (or a few) nft commands and running them individually, in this mode, pbr creates a single atomic nft file (temporary file located at /var/run/pbr.nft and if it contains no errors, the permanent file is installed at /usr/share/nftables.d/ruleset-post/30-pbr.nft), containing all the nft commands that pbr service needs to set up all the policies, dns policies and process custom user files. This file is then just reloaded on any OpenWrt firewall (fw4) reload, without the need to run the pbr init script again.
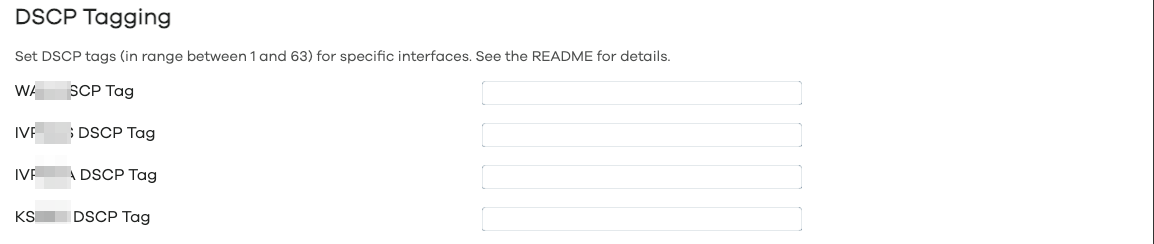
Custom User Files
If the custom user file includes are set, the service will load and execute them after setting up routing and the sets and processing policies. This allows, for example, to add large numbers of domains/IP addresses to nft sets without manually adding all of them to the config file.
The following custom user files are provided:
-
/usr/share/pbr/pbr.user.aws: provided to pull the Continental US AWS IPv4 addresses into the WAN IPv4 sets that the service sets up. -
/usr/share/pbr/pbr.user.netflix: provided to pull the Continental US Netflix IPv4 addresses into the WAN IPv4 sets that the service sets up.
If you want to create your own custom user files, please refer to Processing Custom User Files.
Strict Enforcement
- Supports strict policy enforcement, even if the policy interface is down – resulting in network being unreachable for specific policy (enabled by default).
Use Resolver’s Set Support
- If supported on the system, service can be set to utilize resolver’s set support. Currently supported resolver’s set options are listed below.
Use DNSMASQ nft sets Support
- The
pbrpackage can be configured to utilizednsmasq’snftsetssupport, which requires thednsmasq-fullpackage withnftsetssupport to be installed (see How to install dnsmasq-full). This significantly improves the start up time becausednsmasqresolves the domain names and adds them to the appropriatenftsetin background.dnsmasq’snftsetalso automatically adds third-level domains to theset: ifdomain.comis added to the policy, this policy will affect all*.domain.comsubdomains. This also works for top-level domains (TLDs) as well, a policy targeting theatTLD for example, will affect all the*.atdomains. - Please review the Footnotes/Known Issues section, specifically #5 and #7 and any other information in that section relevant to domain-based routing/DNS.
Customization
- Can be fully configured with
ucicommands or by editing/etc/config/pbrfile. - Has a companion package (
luci-app-pbr) so policies can be configured with Web UI.
Other Features
- Doesn’t stay in memory, creates the routing tables and
nftrules/setsentries which are automatically updated when supported/monitored interface changes. - Proudly made in
 Canada
Canada  , using locally-sourced electrons.
, using locally-sourced electrons.
Screenshots (luci-app-pbr)
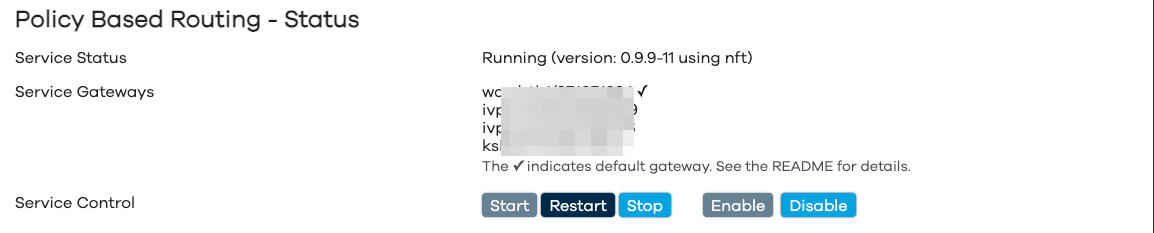
Service Status
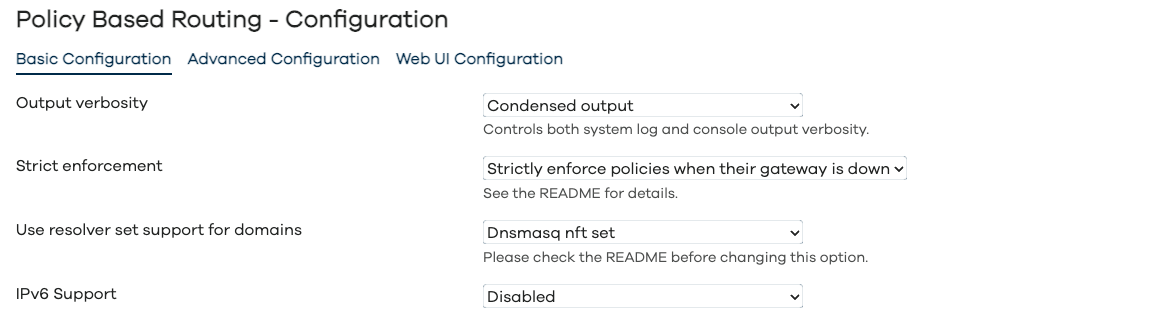
Configuration - Basic Configuration
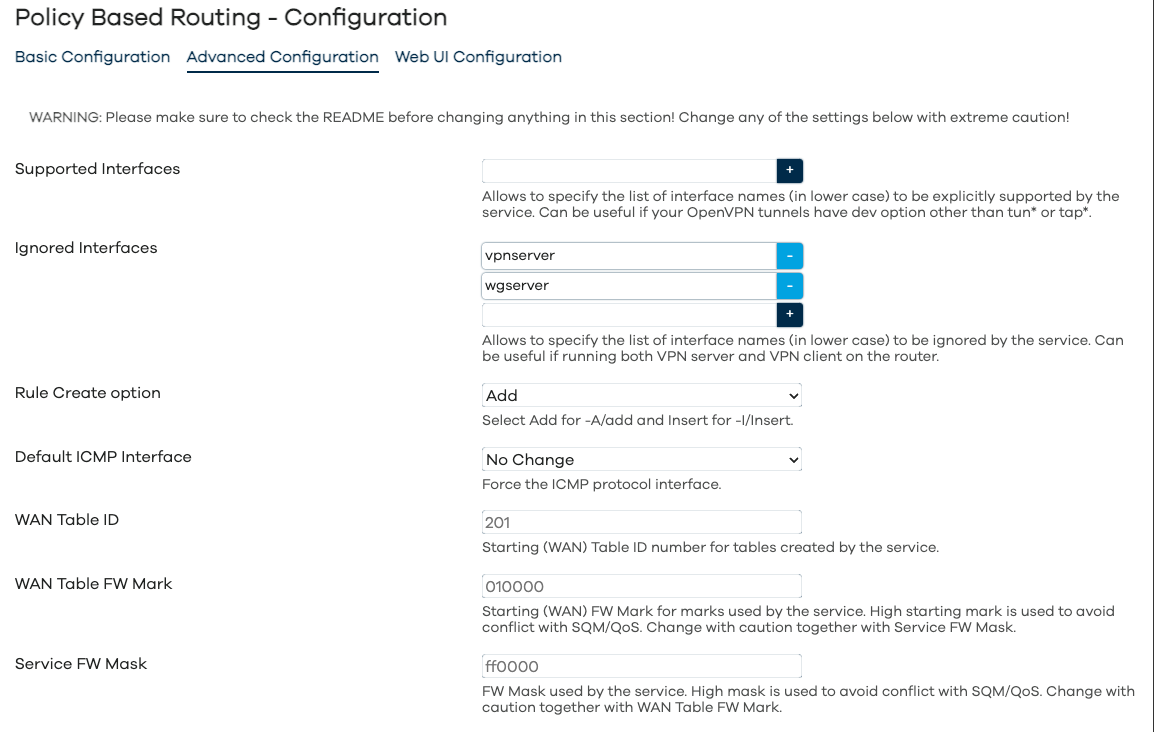
Configuration - Advanced Configuration
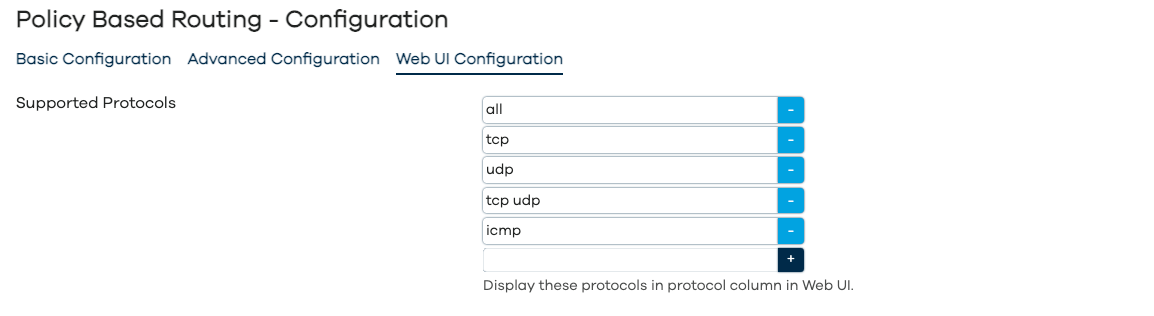
Configuration - WebUI Configuration
Policies
DSCP Tagging
Custom User File Includes
How It Works
How It Works (nft mode)
On start, this service creates routing tables for each supported interface (WAN/WAN6 and VPN tunnels) which are used to route specially marked packets. Rules for the policies are created in the service-specific chains set up by the fw4-specific nft scripts installed with the package. Evaluation of packets happens in these pbr_* chains after which the packets are sent for marking to the pbr_mark_* chains. Whenever possible, the service also creates named sets for dest_addr and src_addr entries and anonymous sets for dest_port and src_port. The service then processes the user-created policies.
Processing Policies
Each policy can result in a new nft rule and possibly an anonymous/in-line or a named nft set to match dest_addr and src_addr. Anonymous/in-line sets may be created within nft rules for dest_port and src_port.
Processing Policies (nft mode)
- Policies with the MAC-addresses, IP addresses, netmasks, local device names or domains will result in a rule targeting named
nftsets. - Policies with non-empty
dest_portandsrc_portwill be created with anonymousnftsetswithin the rule. - The
dnsmasqnftsetentries will be used for domains (if supported and enabled).
Processing DNS Policies
Each DNS policy can result in either a new nft rule and possibly an anonymous/in-line or a named nft set to match src_addr.
If the IP adresses (either legacy IPv4 or IPv6 family or both) are defined in the dest_dns setting for the dns policy, than those addresses will be used to explicitly set the resolver address for a specific DNS policy.
If the network interface is defined in the dest_dns setting for the dns policy, then the first matching-family (either IPv4 or IPv6) DNS server will be used for a specific DNS policy.
Processing DNS Policies (nft mode)
- Policies with the MAC-addresses, IP addresses, netmasks or local device names will result in a rule targeting an anonymous/in-line or a named
nftsets.
Policies Priorities
- The policy priority is the same as its order as listed in Web UI and
/etc/config/pbr. The higher the policy is in the Web UI and configuration file, the higher its priority is. - If set, the
DSCPpolicies is set up first when creating the interface routing. - If enabled, it is highly recommended that the policies with
IGNOREtarget are at the top of the policies list.
Processing Custom User Files
If at least one custom user file is enabled, the service will create the following nft sets and set up the proper routing for them.
Processing Custom User Files (nft mode)
For each interface the service will create nft sets and routing:
-
pbr_interface_4_dst_ip_user: for destination/remote IPv4 addresses and IPv4 CIDR netblocks -
pbr_interface_6_dst_ip_user: for destination/remote IPv6 addresses and IPv6 CIDR netblocks -
pbr_interface_4_src_ip_user: for source/local IPv4 addresses and IPv4 CIDR netblocks -
pbr_interface_6_src_ip_user: for source/local IPv6 addresses and IPv6 CIDR netblocks -
pbr_interface_4_dst_mac_user: for source/local MAC addresses -
pbr_interface_6_dst_mac_user: for source/local MAC addresses
How To Install
How To Install - OpenWrt 23.05 and newer
Please make sure that the requirements are satisfied and install pbr and luci-app-pbr from Web UI or connect to your router via ssh and run the following commands:
opkg update
opkg install pbr luci-app-pbr
How To Install - OpenWrt 22.03 and older
Since this release only supports nft riles and nft sets, it is not recommended to be installed on OpenWrt 22.03 or older. Please use the pbr-iptables package version 1.1.6 or earlier on those systems.
Requirements
Default builds of OpenWrt 23.05 and later are fully compatible with pbr and require no additional packages. If you’re using a non-standard build, you may have to install the following packages on your router: resolveip, ip-full (or a busybox built with ip support).
To satisfy the requirements, connect to your router via ssh and run the following commands:
opkg update; opkg install resolveip ip-full
How to install dnsmasq-full
If you want to use dnsmasq’s nft sets support, you will need to install dnsmasq-full instead of the dnsmasq. To do that, connect to your router via ssh and run the following commands:
opkg update
opkg install libnettle8 libnetfilter-conntrack3
cd /tmp/ && opkg download dnsmasq-full
opkg remove dnsmasq
opkg install dnsmasq-full --cache /tmp/
rm -f /tmp/dnsmasq-full*.ipk
Unmet dependencies
If you are running a development (trunk/snapshot) build of OpenWrt on your router and your build is outdated (meaning that packages of the same revision/commit hash are no longer available and when you try to satisfy the requirements you get errors), please flash either current OpenWrt release image or current development/snapshot image.
How to upgrade to a most recent version
If you’re on OpenWrt 23.05, OpenWrt 24.10 or snapshots and have been advised to upgrade to a pbr/luci-app-pbr versions more recent than what’s available in OpenWrt repositories, please add my packages repository to your OpenWrt device.
How to use
Helpful Instructional Videos
If you want to use WebUI to configure pbr you may want to review the following YouTube videos:
Service Configuration Settings
As per screenshots above, in the Web UI the pbr configuration is split into Basic, Advanced and WebUI settings. The full list of configuration parameters of pbr.config section is:
| Web UI Section | Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | enabled | boolean | 0 | Enable/disable the pbr service. |
| Basic | verbosity | integer | 2 | Can be set to 0, 1 or 2 to control the console and system log output verbosity of the pbr service. |
| Basic | strict_enforcement | boolean | 1 | Enforce policies when their interface is down. See Strict enforcement for more details. |
| Basic | resolver_set | string | dnsmasq.nftset | Configure the use of the resolver’s set support for domains. For most policies targeting domains, this must be enabled to guarantee the reliable operation/routing. Enabling it also speeds up service start-up. Currently supported options are none, and dnsmasq.nftset (see Use Resolver’s Set Support and #7 for more details). Make sure the requirements are met. |
| resolver_instance | list | * | Configure the use of the resolver’s set support for specific instances only by setting a list of instance numbers or names. Currently supported for the following resolver_set options: dnsmasq.nftset. |
|
| Basic | ipv6_enabled | boolean | 0 | Enable/disable IPv6 support. |
| Advanced | supported_interface | list/string | Allows to specify the space-separated list of interface names (in lower case) to be explicitly supported by the pbr service. Can be useful if your OpenVPN tunnels have dev option other than tun*. |
|
| Advanced | ignored_interface | list/string | Allows to specify the space-separated list of interface names (in lower case) to be ignored by the pbr service. Can be useful for an OpenVPN server running on OpenWrt device. WireGuard servers, which have a listen_port defined, are handled automatically, do not add those here. For more information on WireGuard server use cases, please review WireGuard Server Use Cases. |
|
| Advanced | boot_timeout | number | 30 | Allows to specify the time (in seconds) for pbr service to wait for WAN gateway discovery on boot. Can be useful on devices with ADSL modem built in. |
| Advanced | rule_create_option | add/insert | add | Allows to specify the parameter for rules: add for -A in iptables and add in nft and insert for -I in iptables and insert for nft. Add is generally speaking more compatible with other packages/firewall rules. Recommended to change to insert only to enable compatibility with the mwan3 package on OpenWrt 21.02 and earlier. |
| Advanced | icmp_interface | string | Set the default ICMP protocol interface (interface name in lower case). Use with caution. | |
| Hidden | wan_ip_rules_priority | integer | 30000 | Starting (WAN) ip rules priority used by the pbr service. High starting priority is used to avoid conflict with other services, this can be changed by user. |
| Advanced | wan_mark | hexadecimal | 010000 | Starting (WAN) fw mark for marks used by the pbr service. High starting mark is used to avoid conflict with SQM/QoS, this can be changed by user. Change with caution together with fw_mask. |
| Advanced | fw_mask | hexadecimal | ff0000 | FW Mask used by the pbr service. High mask is used to avoid conflict with SQM/QoS, this can be changed by user. Change with caution together with wan_mark. |
| Web UI | webui_show_ignore_target | boolean | 0 | When enabled, show ignore in the list of interfaces. |
| Web UI | webui_supported_protocol | list | 0 | List of protocols to display in the Protocol column for policies. |
| wan_dscp | integer | Allows use of DSCP-tag based policies for WAN interface. | ||
| {interface_name}_dscp | integer | Allows use of DSCP-tag based policies for a VPN interface. | ||
| Hidden | procd_lan_device | list | br-lan | Allows you to override the default br-lan device used for the LAN interface detection. |
| Hidden | procd_reload_delay | integer | 0 | Time (in seconds) for PROCD_RELOAD_DELAY parameter. |
| Hidden | procd_wan_interface | Override wan interface name with this interface. Newer versions do not attempt to auto-detect WAN interface name and setting this from CLI may be required. |
||
| Hidden | procd_wan6_interface | Override wan6 interface name with this interface. |
||
| Hidden | nft_rule_counter | boolean | 0 | Use counter option when creating all nft rules. See nftables wiki for details. |
| Hidden | nft_set_auto_merge | boolean | 1 | Use auto-merge option when creating all nft sets. See nftables wiki for details. |
| Hidden | nft_set_counter | boolean | 0 | Use counter option when creating all nft sets. See nftables wiki for details. |
| Hidden | nft_set_flags_interval | boolean | 1 | Use flags interval option when creating all nft sets. See nftables wiki for details. |
| Hidden | nft_set_flags_timeout | boolean | 0 | Use flags timeout option when creating all nft sets. See nftables wiki for details. |
| Hidden | nft_set_gc_interval | string | Use gc-interval option when creating all nft sets. See nftables wiki for details. |
|
| Hidden | nft_set_policy | string | performance | Set policy option when creating all nft sets. See nftables wiki for details. |
| Hidden | nft_set_timeout | string | Use timeout option when creating all nft sets. See nftables wiki for details. |
Default Settings
Default configuration has service disabled (use Web UI to enable/start service or run uci set pbr.config.enabled=1; uci commit pbr;).
Policy Options
Each policy may have a combination of the options below, the name and interface options are required.
The src_addr, src_port, dest_addr and dest_port options supports parameter negation, for example if you want to exclude remote port 80 from the policy, set dest_port to "!80" (notice lack of space between ! and parameter).
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | Policy name, it must be set. | |
| enabled | 1 | Enable/disable policy. To display the Enable checkbox column for policies in the WebUI, make sure to select Enabled for Show Enable Column in the Web UI tab. |
| interface | Policy interface, it must be set. | |
| src_addr | List of space-separated local/source IP addresses, CIDRs, hostnames or mac addresses (colon-separated). You can also specify a local physical device (like a specially created wlan) prepended by an @ symbol. Versions 1.1.2 and later allow using URLs to list of addresses. If curl is installed you can use the file:// schema, otherwise you can use ftp://, http:// and https:// schemas (which are obviously not compatible with the secure_reload option). |
|
| src_port | List of space-separated local/source ports or port-ranges. | |
| dest_addr | List of space-separated remote/target IP addresses, CIDRs or hostnames/domain names. Versions 1.1.2 and later allow using URLs to list of addresses. If curl is installed you can use the file:// schema, otherwise you can use ftp://, http:// and https:// schemas. This is obviously not compatible with the secure_reload option. |
|
| dest_port | List of space-separated remote/target ports or port-ranges. | |
| proto | auto | Policy protocol, can be any valid protocol from /etc/protocols for CLI/uci or can be selected from the values set in webui_supported_protocol. |
| chain | prerouting | Policy chain, can be either forward, input, prerouting, postrouting or output. This setting is case-sensitive. |
DNS Policy Options
Each policy may have a combination of the options below, the name, the src_addr and dest_dns options are required.
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | DNS Policy name, it must be set. | |
| enabled | 1 | Enable/disable DNS policy. To display the Enable checkbox column for policies in the WebUI, make sure to select Enabled for Show Enable Column in the Web UI tab. |
| src_addr | List of space-separated local/source IP addresses, CIDRs, hostnames or mac addresses (colon-separated). You can also specify a local physical device (like a specially created wlan) prepended by an @ symbol. You can use URLs to list of addresses. If curl is installed you can use the file:// schema, otherwise you can use ftp://, http:// and https:// schemas (which are obviously not compatible with the secure_reload option). |
|
| dest_dns | List of space-separated IPv4/IPv6 addresses for resolvers used for the DNS policy or a network interface, which DNS server(s) will be used for the DNS policy. |
Custom User Files Include Options
| Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| path | Path to a custom user file (in a form of shell script), it must be set. | |
| enabled | 1 | Enable/disable setting. |
Example Policies
Single IP, IP Range, Local Machine, Local MAC Address
The following policies route traffic from a single IP address, a range of IP addresses, a local machine (requires definition as DHCP host record in DHCP config), a MAC-address of a local device and finally all of the above via WAN.
config policy
option name 'Local IP'
option interface 'wan'
option src_addr '192.168.1.70'
config policy
option name 'Local Subnet'
option interface 'wan'
option src_addr '192.168.1.81/29'
config policy
option name 'Local Machine'
option interface 'wan'
option src_addr 'dell-ubuntu'
config policy
option name 'Local MAC Address'
option interface 'wan'
option src_addr '00:0F:EA:91:04:08'
config policy
option name 'Local Devices'
option interface 'wan'
option src_addr '192.168.1.70 192.168.1.81/29 dell-ubuntu 00:0F:EA:91:04:08'
SIP Port
The following policy routes standard SIP port traffic via WAN for both TCP and UDP protocols.
config policy
option name 'SIP Ports'
option interface 'wan'
option dest_port '5060'
option proto 'tcp udp'
Plex Media Server
The following policies route Plex Media Server traffic via WAN. Please note, you’d still need to open the port in the firewall either manually or with the UPnP.
config policy
option name 'Plex Local Server'
option interface 'wan'
option src_port '32400'
config policy
option name 'Plex Remote Servers'
option interface 'wan'
option dest_addr 'plex.tv my.plexapp.com'
Emby Media Server
The following policy route Emby traffic via WAN. Please note, you’d still need to open the port in the firewall either manually or with the UPnP.
config policy
option name 'Emby Local Server'
option interface 'wan'
option src_port '8096 8920'
config policy
option name 'Emby Remote Servers'
option interface 'wan'
option dest_addr 'emby.media app.emby.media tv.emby.media'
Ignore Target
The service allows you to set an interface for a specific policy to ignore to skip further processing of matched traffic. This option needs to be explicitly enabled for use in WebUI, check Service Configuration Settings for details. Some use cases are listed below.
Ignore Requests
The following policy allows you to skip processing some requests (like traffic to an OpenVPN or WireGuard server running on the router):
config pbr 'config'
...
option webui_show_ignore_target '1'
config policy
option name 'Ignore Local Requests by Destination'
option interface 'ignore'
option dest_addr '192.168.200.0/24'
Please note, you need to enable Show Ignore Target option for the WebUI to listignore\ in the list of gateways.
It’s a good idea to keep the policies targeting ignore interface at the top of the config file/list of policies displayed in WebUI to make sure they are processed first.
Netflix Domains
The following policy should route US Netflix traffic via WAN. For capturing international Netflix domain names, you can refer to the getdomainnames.sh-specific instructions on GitHub/jsDelivr and don’t forget to adjust them for OpenWrt. This may not work if Netflix changes things. For more reliable US Netflix routing you may want to consider also using custom user files.
config policy
option name 'Netflix Domains'
option interface 'wan'
option dest_addr 'amazonaws.com netflix.com nflxext.com nflximg.net nflxso.net nflxvideo.net dvd.netflix.com'
Example Custom User Files Includes
config include
option path '/etc/pbr/pbr.user.aws'
option enabled '0'
config include
option path '/etc/pbr/pbr.user.netflix'
option enabled '0'
Example OpenWrt Configurations for More Complex Cases
WireGuard Server Use Cases
Yes, I’m aware that in terms of topology there are no clients nor servers in WireGuard, it’s all peers. However, if one of the WireGuard instances has the listen_port, we’d call this one a server and if it doesn’t have the listen_port, then it’s a client.
The pbr service automatically detects the WireGuard server and without any customizations the default behaviour is:
- do not show the WireGuard server interfaces in the list of interfaces available for policies/DSCP tagging.
- to create an ip rule to send traffic from WireGuard server over WAN to ensure that your WireGuard server is still accessible/functional even if your default gateway is a tunnel and not a WAN connection.
However, there could be use cases where this default behaviour is not desired and needs to be altered, they are addressed below
WireGuard Server Use Case: Targeting in Policies
If you need to target the WireGuard server in policies, please add its interface name to Supported Interface option. That way the ip rule to send traffic from WireGuard server over WAN will still be automatically created, but the WireGuard server name will appear/can be targeted in policies.
WireGuard Server Use Case: Disable IP Rule for WAN
If you need to send the WireGuard server traffic over default gateway (and not WAN), in other words you want to disable the automatic ip rule to send traffic from WireGuard server over WAN, add the WireGuard server interface name to Ignored Interface option.
WireGuard Server Use Case: Targeting in Policies and Disable IP Rule for WAN
If you need to target the WireGuard server in policies and you need to send the WireGuard server traffic over default gateway (and not WAN), add the WireGuard server interface name to both Supported Interface and Ignored Interface options.
Basic OpenVPN Client Config
There are multiple guides online on how to configure the OpenVPN client on OpenWrt “the easy way”, and they usually result either in a kill-switch configuration or configuration where the OpenVPN tunnel cannot be properly (and separately from WAN) routed, either way, incompatible with the Policy-Based Routing.
Below is the sample OpenVPN client configuration for OpenWrt which is guaranteed to work. If you have already deviated from the instructions below (ie: made any changes to any of the wan or lan configurations in either /etc/config/network or /etc/config/firewall), you will need to start from scratch with a fresh OpenWrt install.
Relevant part of /etc/config/pbr:
config pbr 'config'
list supported_interface 'vpnclient'
...
The recommended network/firewall settings are below.
Relevant part of /etc/config/network (DO NOT modify default OpenWrt network settings for either wan or lan):
config interface 'vpnclient'
option proto 'none'
option device 'ovpnc0'
Relevant part of /etc/config/firewall:
config zone
option name 'wan'
list network 'wan'
list network 'vpnclient'
...
Relevant part of /etc/config/openvpn (configure the rest of the client connection for your specifics by either referring to an existing .ovpn file or thru the OpenWrt uci settings):
config openvpn 'vpnclient'
option enabled '1'
option client '1'
option dev_type 'tun'
option dev 'ovpnc0'
...
Multiple OpenVPN Clients
If you use multiple OpenVPN clients on your router, the order in which their devices are named (tun0, tun1, etc) is not guaranteed by OpenWrt. The following settings are recommended in this case.
For /etc/config/network:
config interface 'vpnclient0'
option proto 'none'
option device 'ovpnc0'
config interface 'vpnclient1'
option proto 'none'
option device 'ovpnc1'
For /etc/config/openvpn:
config openvpn 'vpnclient0'
option client '1'
option dev_type 'tun'
option dev 'ovpnc0'
...
config openvpn 'vpnclient1'
option client '1'
option dev_type 'tun'
option dev 'ovpnc1'
...
For /etc/config/pbr:
config pbr 'config'
list supported_interface 'vpnclient0 vpnclient1'
...
Local OpenVPN Server + OpenVPN Client (Scenario 1)
If the OpenVPN client on your router is used as default routing (for the whole Internet), make sure your settings are as following (three dots on the line imply other options can be listed in the section as well).
Relevant part of /etc/config/pbr:
config pbr 'config'
list ignored_interface 'vpnserver'
...
config policy
option name 'OpenVPN Server'
option interface 'wan'
option proto 'tcp'
option src_port '1194'
option chain 'output'
The network/firewall/openvpn settings are below.
Relevant part of /etc/config/network (DO NOT modify default OpenWrt network settings for either wan or lan):
config interface 'vpnclient'
option proto 'none'
option device 'ovpnc0'
config interface 'vpnserver'
option proto 'none'
option device 'ovpns0'
option auto '1'
Relevant part of /etc/config/firewall:
config zone
option name 'lan'
list network 'lan'
list network 'vpnserver'
...
config zone
option name 'wan'
list network 'wan'
list network 'vpnclient'
...
config rule
option name 'Allow-OpenVPN-Inbound'
option target 'ACCEPT'
option src '*'
option proto 'tcp'
option dest_port '1194'
Relevant part of /etc/config/openvpn:
config openvpn 'vpnclient'
option client '1'
option dev_type 'tun'
option dev 'ovpnc0'
option proto 'udp'
option remote 'some.domain.com 1197' # DO NOT USE PORT 1194 for VPN Client
...
config openvpn 'vpnserver'
option port '1194'
option proto 'tcp'
option server '192.168.200.0 255.255.255.0'
...
Local OpenVPN Server + OpenVPN Client (Scenario 2)
If the OpenVPN client is not used as default routing and you create policies to selectively use the OpenVPN client, make sure your settings are as following (three dots on the line imply other options can be listed in the section as well). Make sure that the policy mentioned below is at the top of your policies list.
Relevant part of /etc/config/pbr:
config pbr 'config'
list ignored_interface 'vpnserver'
...
config policy
option name 'Ignore Local Traffic'
option interface 'ignore'
option dest_addr '192.168.200.0/24'
...
The network/firewall/openvpn settings are below.
Relevant part of /etc/config/network (DO NOT modify default OpenWrt network settings for either wan or lan):
config interface 'vpnclient'
option proto 'none'
option device 'ovpnc0'
config interface 'vpnserver'
option proto 'none'
option device 'ovpns0'
option auto '1'
Relevant part of /etc/config/firewall:
config zone
option name 'lan'
list network 'lan'
list network 'vpnserver'
...
config zone
option name 'wan'
list network 'wan'
list network 'vpnclient'
...
config rule
option name 'Allow-OpenVPN-Inbound'
option target 'ACCEPT'
option src '*'
option proto 'tcp'
option dest_port '1194'
Relevant part of /etc/config/openvpn:
config openvpn 'vpnclient'
option client '1'
option dev_type 'tun'
option dev 'ovpnc0'
option proto 'udp'
option remote 'some.domain.com 1197' # DO NOT USE PORT 1194 for VPN Client
list pull_filter 'ignore "redirect-gateway"' # for OpenVPN 2.4 and later
option route_nopull '1' # for OpenVPN earlier than 2.4
...
config openvpn 'vpnserver'
option port '1194'
option proto 'tcp'
option server '192.168.200.0 255.255.255.0'
...
Footnotes/Known Issues
-
If your
OpenVPNinterface has the device name different from tun*, is not up and is not explicitly listed insupported_interfaceoption, it may not be available in the policiesInterfacedrop-down within WebUI. -
If your default routing is set to the VPN tunnel, then the true WAN interface cannot be discovered using OpenWrt built-in functions, so service will assume your network interface ending with or starting with
wanis the true WAN interface. -
The service does NOT support the “killswitch” router mode (where there is no firewall forwarding from
laninterface towaninterface, so if you stop the VPN tunnel, you have no Internet connection). For proper operation, leave all the default OpenWrtnetworkandfirewallsettings forlanandwanintact. -
When using the
dnsmasq.nftsetoption, please make sure to flush the DNS cache of the local devices, otherwise domain policies may not work until you do. If you’re not sure how to flush the DNS cache (or if the device/OS doesn’t offer an option to flush its DNS cache), reboot your local devices when starting to use the service and/or when connecting data-capable device to your WiFi. -
When using the policies targeting physical devices, you may need to make sure you have the following packages installed:
kmod-br-netfilter,kmod-ipt-physdevandiptables-mod-physdev. Also, if your physical device is a part of the bridge, you may have to setnet.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptablesto1in your/etc/sysctl.conf. -
If you’re using domain names in the
dest_addroption of the policy, it is recommended to usednsmasq.nftsetoptions forresolver_set. Otherwise, the domain name will be resolved when the service starts up and the resolved IP address(es) will be added to an apropriate set or aniptablesornftrule. Resolving a number of domains on start is a time consuming operation, while using thednsmasq.nftsetoptions allows transparent and fast addition of the correct domain IP addresses to the apropriate set on DNS request or when resolver is idle. -
When service is started, it subscribes to the supported interfaces updates thru the PROCD. While I was never able to reproduce the issue, some customers report that this method doesn’t always work in which case you may want to set up iface hotplug script to reload service when the relevant interface(s) are updated.
FAQ
You may find some useful information below.
A Word About Default Routing
Service does not alter the default routing. Depending on your VPN tunnel settings (and settings of the VPN server you are connecting to), the default routing might be set to go via WAN or via VPN tunnel. This service affects only routing of the traffic matching the policies. If you want to override default routing, follow the instructions below.
OpenVPN tunnel configured via uci (/etc/config/openvpn)
To unset an OpenVPN tunnel as default route, set the following to the appropriate section of your /etc/config/openvpn:
-
For OpenVPN 2.4 and newer client config:
list pull_filter 'ignore "redirect-gateway"' -
For OpenVPN 2.3 and older client config:
option route_nopull '1' -
For your WireGuard (client) config:
option route_allowed_ips '0'
OpenVPN tunnel configured with .ovpn file
To unset an OpenVPN tunnel as default route, set the following to the appropriate section of your .ovpn file:
-
For OpenVPN 2.4 and newer client
.ovpnfile:pull-filter ignore "redirect-gateway" -
For OpenVPN 2.3 and older client
.ovpnfile:route-nopull
WireGuard tunnel
To unset a WireGuard tunnel as default route, set the following to the appropriate section of your /etc/config/network:
-
For your WireGuard (client) config:
option route_allowed_ips '0' -
Routing WireGuard traffic may require setting
net.ipv4.conf.wg0.rp_filter = 2in/etc/sysctl.conf. Please refer to issue #41 for more details.
A Word About Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1 App
Cloudflare has released an app for iOS and Android, which can also be configured to route traffic thru their own VPN tunnel (WARP+).
If you use Cloudflare’s VPN tunnel (WARP+), none of the policies you set up with the VPN Policy Routing will take effect on your mobile device. Disable WARP+ for your home WiFi to keep VPN Policy Routing affecting your mobile device.
If you just use the private DNS queries (WARP), A Word About DNS-over-HTTPS applies. You can also disable WARP for your home WiFi to keep VPN Policy Routing affecting your mobile device.
A Word About DNS-over-HTTPS
Some browsers, like Mozilla Firefox or Google Chrome/Chromium have DNS-over-HTTPS proxy built-in. Their requests to web-sites listed in policies cannot be properly routed if the resolver_set is set to dnsmasq.nftset. To fix this, you can try either of the following:
-
Disable the DNS-over-HTTPS support in your browser and use the OpenWrt’s
net/https-dns-proxy(README on GitHub/jsDelivr) package with optionalluci-app-https-dns-proxyWebUI/luci app. You can then continue to usednsmasq.nftsetsetting for theresolver_setin Policy-Based Routing. -
Continue using DNS-over-HTTPS in your browser (which, by the way, also limits your options for router-level AdBlocking as described in
net/adblock-fastREADME on GitHub/jsDelivr), you than would either have to switch theresolver_settonone. Please note, you will lose all the benefits of the Resolver Set Support option.
A Word About HTTP/3 (QUIC)
If you want to target traffic using HTTP/3 protocol, you can use the AUTO as the protocol (the policy will be either protocol-agnostic or TCP/UDP) or explicitly use UDP as a protocol.
A Word About IPv6 Routing
Due to the nature of IPv6, it’s not supposed to be routed as IPv4 is with this package. A fellow user has graciously contributed a gist detailing their experience to get IPv6 routing working.
A Word About Routing Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu Traffic
There are two following scenarios with VPN connections and Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu traffic.
Routing Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu Traffic via VPN Tunnel
If you live in a country where Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu are not available and want to circumvent geo-fencing, this package can’t help you. The Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu do a great job detecting VPN usage when accessing their services and circumventing geographical restrictions is not only dubiously legal, it’s also technically very challenging.
Routing Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu Traffic via WAN
If you live in a country where Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu are available, you obviously do NOT want to use VPN tunnel for their traffic.
If the VPN tunnel is not used as a default gateway on your router, you should not have a problem accessing Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu (just make sure that your DNS requests are not routed via VPN tunnel either).
If the VPN tunnel is used as a default gateway, either:
- send ALL traffic from your multimedia devices (by using their IP addresses or device names in the
src_addroption in config file or Local addresses /devices field in WebUI) accessing Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu to WAN; this is the more reliable and recommended method. - use the Netflix/AWS custom user files in combination with the Netflix/Amazon Prime/Hulu domains and
dnsmasq.nftsetoption to route traffic to Netflix/Amazon via WAN; this is definitely less reliable method and may not work in all regions.
Either way make sure that your DNS requests are not routed via VPN Tunnel!
A Word About Interface Hotplug Script
Sometimes#8 the service doesn’t get reloaded when supported interfaces go up or down. This can be an annoying experience since the service may start before all supported VPN connections are up and then not get updated when the VPN connections get established. In that case, run the following command from CLI to create the interface hotplug script to cause the service to be reloaded in interface updates:
mkdir -p /etc/hotplug.d/iface/
cat << 'EOF' > /etc/hotplug.d/iface/70-pbr
!/bin/sh
logger -t pbr "Reloading $INTERFACE due to $ACTION of $INTERFACE ($DEVICE)"
/etc/init.d/pbr reload_interface "$INTERFACE"
EOF
A Word About Broken Domain Policies
For the domain policies to successfully work, you need:
- a
dnsmasq-fullinstalled on your router. - a
pbrversion compatible with thednsmasq-full. - a policy containing domain name(s) defined in the
pbrconfig. - a local (LAN/WLAN) client to make a DNS request to your router to resolve the domain(s) defined in the
pbrpolicy.
Some examples on when the domain(s) policies defined in pbr may not work:
- when regular
dnsmasqand notdnsmasq-fullis installed. - installed
pbris not compatible with the installeddnsmasq-full(ie:dnsmasq-fullsupports nft sets, but you havepbr-iptablesinstalled). - you don’t have a policy containing domain name(s) defined in the
pbrconfig. - you have a DNS Policy set for a local device, so its DNS requests are not being sent to
dnsmasq-full. - you have a domain name(s) based policy configured for LAN device(s), but are testing from the LAN device which is not affected by the policy or testing from the router.
- a local (LAN/WLAN) client does not make a DNS request to your router, this is probably the most common cause and there could be a few reasons for the DNS requests to not reach router:
- a local client has the DNS response cached, solved by rebooting the client.
- a local client is set to use a DNS different from router thru option 6 defined in router
dhcpsettings, solved by editing your router’sdhcpconfig. - a local client is set to use a DNS different from router thru the DNS explicitly set on client, solved by removing explicit DNS set on client.
- a local client is set to use an ecnrypted DNS, solved by disabling use of encrypted DNS requests.
- a local client uses the hardcoded DNS servers which you cannot edit, solved by enabling DNS hijacking on your router.
Getting Help
General discussion of this package is happening at the OpenWrt forum thread.
If things are not working as intended, please first set counters to 1 and verbosity to 2 by running these commands:
uci set pbr.config.nft_rule_counter='1'
uci set pbr.config.nft_set_counter='1'
uci set pbr.config.verbosity='2'
uci commit pbr
and then run the following commands and include their output (you can and should mask sensitive information) in your post:
ubus call system board
uci export dhcp
uci export firewall
uci export network
uci export pbr
/etc/init.d/pbr status
/etc/init.d/pbr reload
/etc/init.d/pbr status
If you want to encrypt the files before sharing them, you can do so with the commands below (you’ll need to have OpenSSL installed on your router):
openssl rand 214 > /tmp/keyfile.key
wget -O /tmp/dev.melmac.net.pem https://dev.melmac.net/repo/dev.melmac.net.pem
openssl pkeyutl -encrypt -inkey /tmp/dev.melmac.net.pem -pubin -in /tmp/keyfile.key -out /tmp/keyfile.enc
openssl enc -in /etc/config/dhcp -out /tmp/dhcp.enc -e -aes256 -pbkdf2 -kfile /tmp/keyfile.key
openssl enc -in /etc/config/firewall -out /tmp/firewall.enc -e -aes256 -pbkdf2 -kfile /tmp/keyfile.key
openssl enc -in /etc/config/network -out /tmp/network.enc -e -aes256 -pbkdf2 -kfile /tmp/keyfile.key
openssl enc -in /etc/config/pbr -out /tmp/pbr.enc -e -aes256 -pbkdf2 -kfile /tmp/keyfile.key
Then share the following files: /tmp/keyfile.enc, /tmp/dhcp.enc, /tmp/firewall.enc, /tmp/network.enc, /tmp/pbr.enc.
First Troubleshooting Step
If your router is set to use default routing via VPN tunnel and the WAN-targeting policies do not work, you need to stop your VPN tunnel first and ensure that you still have an Internet connection. If your router is set up to use default routing via a VPN tunnel and when you stop the VPN tunnel you have no Internet connection, this package can’t help you. You first need to make sure that you do have an Internet connection when the VPN tunnel is stopped.
Donate
If you find pbr useful, please consider donating to support development of this project. I’ve been developing it in my spare time without any external funding, outside of my GitHub sponsors. You can donate by:
- Sponsoring me on GitHub with monthly donation.
- Sponsoring me on GitHub with one-time donation.
- Sending a donation thru PayPal.
Error Messages Details
Warning Messages Details
Warning: Please set ‘dhcp.lan.force=1’
If the dhcp.lan.force is set to 1, this speeds up the dnsmasq start/restart times and in turn speeds up the pbr service start/reload/restart times. To make things faster, run:
uci set dhcp.lan.force='1'
uci commit dhcp
If your LAN interface name(s) are different from lan, adjust the command above.
Thanks
I’d like to thank everyone who helped by providing testing and feedback on this service. Without contributions from @hnyman, @dibdot, @danrl, @tohojo, @cybrnook, @nidstigator, @AndreBL, @dz0ny, @tew42, bogorad, rigorous testing/bugreporting by @dziny, @bluenote73, @buckaroo, @Alexander-r, @n8v8R, psherman, @Vale-max, @aliicex, dscpl, pesa1234 and multiple contributions from @egc112, @bigsmile74, @dl12345 and trendy and feedback from other OpenWrt users it wouldn’t have been possible. WireGuard/IPv6 support is courtesy of IVPN.